
Throughout fiscal year 2021, the company issued no new shares and repurchased 20 million shares, resulting in 140 million common shares outstanding at the end of the period. ABC also has 1 million stock options outstanding with an exercise price of $10, while its stock trades at $20. In that case, the options are excluded because they would increase the diluted share count — and thus actually decrease the loss per share. In that event, the higher diluted share count is making the business look better than it might otherwise be. The accounting rules applied to diluted shares aim to prevent that outcome. For both basic EPS and diluted EPS, the earnings figure should be the same.
What factors can impact EPS?
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Common shareholders have voting rights to elect the Board of Directors and pass (or reject) corporate policies brought to vote by shareowners.
Diluted Earnings Per Share Calculation Example (EPS)
EPS is a critical metric for investors as it provides a direct measure of a company’s profitability. The higher the EPS, the more profitable the company is perceived to be, potentially making its stock more attractive to investors. Finally, the Return on Equity (ROE) ratio measures a company’s efficiency in generating profits from shareholders’ equity, supplementing the profitability perspective provided by EPS. Still, adjusted EPS can sometimes provide a better “look-through” on the company’s profitability and performance, if the metric is not abused by management teams.
When to use basic, diluted or adjusted EPS
Earnings season is the Wall Street equivalent of a school report card. It happens four times per year; publicly traded companies in the U.S. are required by law to report their optimal choice of entity for the qbi deduction financial results on a quarterly basis. Most companies follow the calendar year for reporting, but they do have the option of reporting based on their own fiscal calendars.
- On the other hand, while the figure is accurate, the trailing EPS is often considered old news.
- This tool will teach you how to calculate your earnings per share and provide you with a foolproof EPS formula.
- On the other hand, diluted earnings per share represent the profit that would be earned by each share of common stock if all dilutive securities were converted into common stock.
What is your current financial priority?
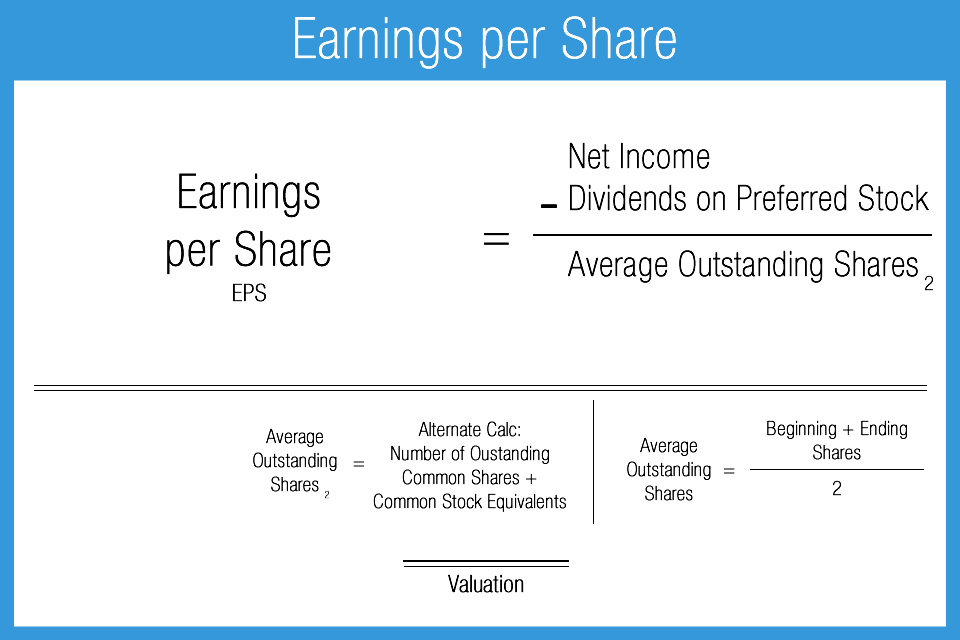
Earnings per share (EPS) is a company’s net income divided by its outstanding shares of common stock. Net income is the income available to all shareholders after a company’s costs and expenses are accounted for. We now have the necessary inputs to calculate the basic EPS, so we’ll divide the net earnings for common equity by the weighted average shares outstanding. The Earnings Per Share (EPS) is the ratio between the net profit generated by a company and the total number of common shares outstanding.
Investors need to look at both basic and diluted EPS to get a clearer picture of a company’s financial health. The earnings per share ratio will help that investor understand the capacity a company has for higher dividends in the future. It is a tool that is used frequently by investors, but is by no means the only measure of a company’s financial future. You should take into account all of the financial information available to make an investment decision.
To calculate a company’s earnings per share, take a company’s net income and subtract from that preferred dividend. When calculating EPS, sometimes investors may use the weighted average of shares at the beginning and ending period being measured (say, a full year) in the denominator to give a broader picture of EPS. Other times, investors use the number of shares at the end of the period since it’s the most current and it’s the figure that the company is moving forward with. Although many investors don’t pay much attention to the EPS, a higher earnings per share ratio often makes the stock price of a company rise. Since so many things can manipulate this ratio, investors tend to look at it but don’t let it influence their decisions drastically. When calculating the quarterly EPS for a company, using the weighted average shares outstanding for the time period may give you a better picture than the shares outstanding on the last day of the quarter.
The article was reviewed, fact-checked and edited by our editorial staff prior to publication. Neither the author nor editor held positions in the aforementioned investments at the time of publication. Bank of America (BAC), for example, is in the financial services sector. Investors can compare the EPS of Bank of America with other financial institutions, such as JP Morgan Chase (JPM) or Wells Fargo (WFC), to get an idea of relative financial strength.
